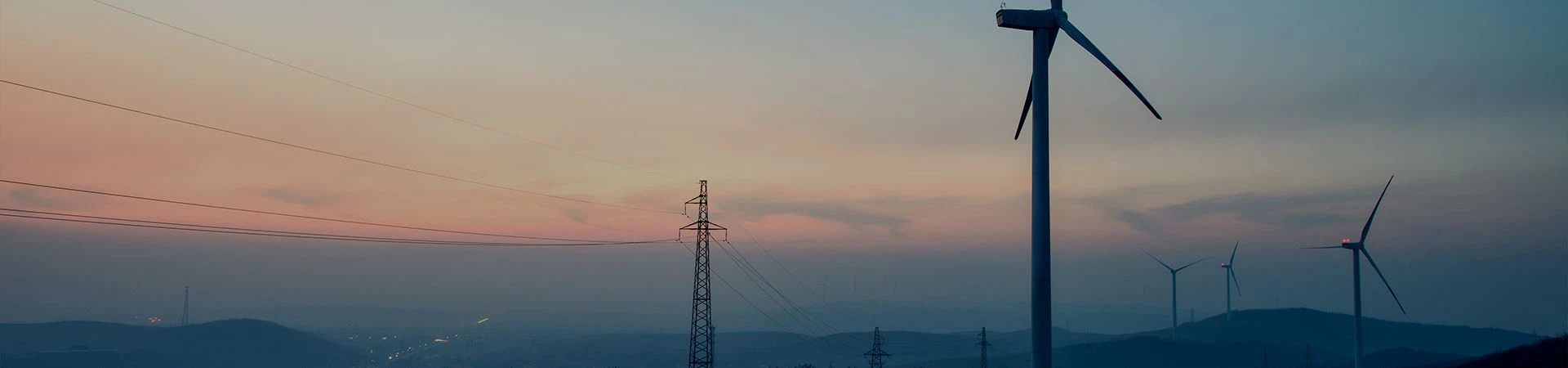
The main reasons why bare conductors are often used on high-voltage transmission line towers are as follows:
Excellent conductivity: Bare conductors are usually made of good conductors such as aluminum or copper, with low resistance, which can effectively reduce power loss.
Strong heat dissipation ability: Because there is no insulation layer, the bare conductor has good heat dissipation effect, which can dissipate the heat generated by the flow of current faster and prevent overheating.
Wind and ice resistance: Bare conductors can withstand large wind and ice and snow loads, and can remain stable under severe weather conditions.
Convenient construction and maintenance: Bare conductors are relatively simple, and construction and maintenance can be more convenient, especially when there is no complexity of insulation treatment during high-altitude operations.
Low cost: Compared with insulated conductors, bare conductors have lower manufacturing and construction costs and are suitable for large-scale high-voltage transmission systems.
Strong environmental adaptability: In an open high-voltage transmission environment, bare conductors will not be affected by insulation aging, shedding and other problems, and have better reliability.
These advantages make bare conductors a common choice for high-voltage transmission systems.